| Species |
Homo sapiens |
| Alternate Name(s) |
GAD, GAD25, GAD67 |
| Description |
glutamate decarboxylase 1
|
| Chromosome |
2
|
| Locus |
2q31 |
| Rat Homolog |
Gad1
|
| Worm Homolog |
unc-25
|
| Protein Alignment |
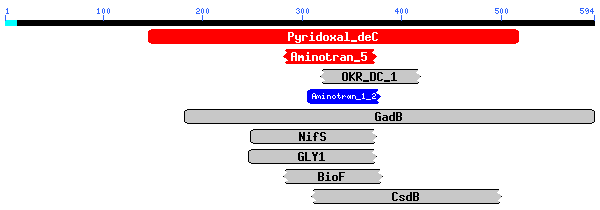
Homo sapiens:
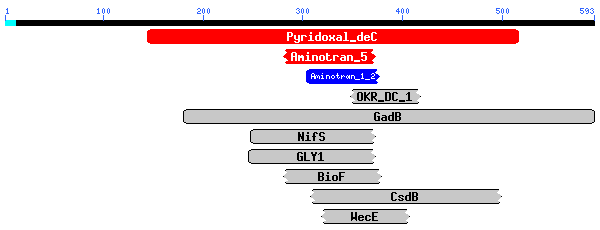
Mus musculus:
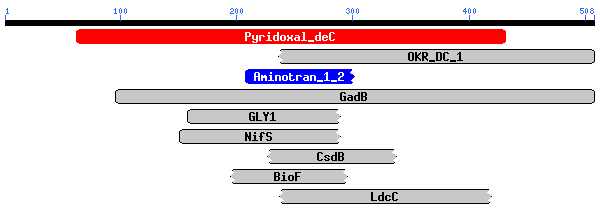
Caenorhabditis elegans:
 |
| Reference(s) |
Battaglioli G, Rosen DR, Gospe SM Jr, Martin DL. Glutamate decarboxylase is not genetically linked to pyridoxine-dependent seizures. Neurology. 2000 Jul 25;55(2):309-11.
Cormier-Daire V, Dagoneau N, Nabbout R, Burglen L, Penet C, Soufflet C, Desguerre I, Munnich A, Dulac O. A gene for pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy maps to chromosome 5q31. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Oct;67(4):991-3. Epub 2000 Sep 07.
Lynex CN, Carr IM, Leek JP, Achuthan R, Mitchell S, Maher ER, Woods CG, Bonthron DT, Markham AF. Homozygosity for a mis-sense mutation in the 67kDa isoform of glutamate decarboxylase in a family with autosomal recessive spastic cerebral palsy: parallels with Stiff-Person Syndrome and other movement disorders. BMC Neurol. 2004 Nov 30;4(1):20 [Epub ahead of print].
Mi J, Chatterjee S, Wong KK, Forbes C, Lawless G, Tobin AJ. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) drives constitutive production of glutamate decarboxylase in neural cell lines. J Neurosci Res. 1999 Jul 1;57(1):137-48.
Neder L, Valente V, Carlotti CG Jr, Leite JP, Assirati JA, Paco-Larson ML, Moreira JE. Glutamate NMDA receptor subunit R1 and GAD mRNA expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Dec;22(5-6):689-98.
|
