| Species |
Homo sapiens |
| Alternate Name(s) |
PAFAH1B1, MDCR, PAFAH, MDS |
| Epilepsy-Associated Disorder(s) |
classical lissencephaly (Miller-Dieker syndrome) |
| Description |
platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, isoform Ib, alpha subunit 45kDa
|
| Chromosome |
17
|
| Locus |
17p13.3 |
| Mouse Homolog |
Lis1
|
| Worm Homolog |
lis-1
|
| Protein Alignment |
Homo sapiens:
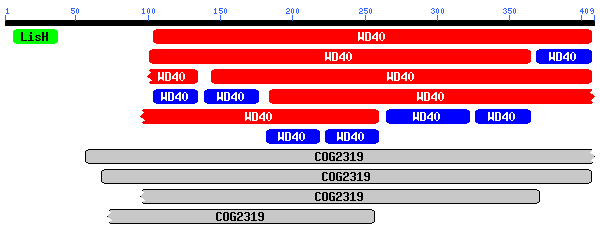
Mus musculus:
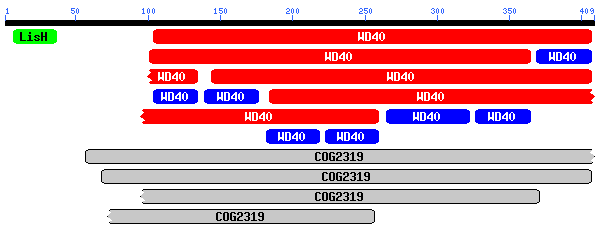
Caenorhabditis elegans:
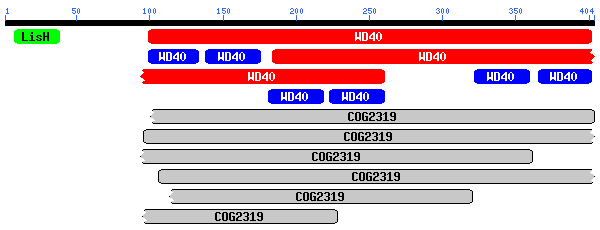 |
| Reference(s) |
Cardoso C, Leventer RJ, Matsumoto N, Kuc JA, Ramocki MB, Mewborn SK, Dudlicek LL, May LF, Mills PL, Das S, Pilz DT, Dobyns WB, Ledbetter DH. The location and type of mutation predict malformation severity in isolated lissencephaly caused by abnormalities within the LIS1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Dec 12;9(20):3019-28.
Caspi M, Coquelle FM, Koifman C, Levy T, Arai H, Aoki J, De Mey JR, Reiner O. LIS1 missense mutations: variable phenotypes result from unpredictable alterations in biochemical and cellular properties. J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 3;278(40):38740-8. Epub 2003 Jul 28.
Coquelle FM, Caspi M, Cordelieres FP, Dompierre JP, Dujardin DL, Koifman C, Martin P, Hoogenraad CC, Akhmanova A, Galjart N, De Mey JR, Reiner O. LIS1, CLIP-170's key to the dynein/dynactin pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(9):3089-102.
Gambello MJ, Darling DL, Yingling J, Tanaka T, Gleeson JG, Wynshaw-Boris A. Multiple dose-dependent effects of Lis1 on cerebral cortical development. J Neurosci. 2003 Mar 1;23(5):1719-29.
Guerrini R, Carrozzo R. Epileptogenic brain malformations: clinical presentation, malformative patterns and indications for genetic testing. Seizure. 2002 Apr;11 Suppl A:532-43; quiz 544-7.
Lo Nigro C, Chong CS, Smith AC, Dobyns WB, Carrozzo R, Ledbetter DH. Point mutations and an intragenic deletion in LIS1, the lissencephaly causative gene in isolated lissencephaly sequence and Miller-Dieker syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Feb;6(2):157-64.
King A, Upadhyaya M, Penney C, Doshi R. A case of Miller-Dieker syndrome in a family with neurofibromatosis type I. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2000 Apr;99(4):425-7.
Locke CJ, Williams SN, Schwarz EM, Caldwell GA, Caldwell KA. Genetic interactions among cortical malformation genes that influence susceptibility to convulsions in C. elegans. Brain Res. 2006 Sep 20; [Epub ahead of print]
Pancoast M, Dobyns W, Golden JA. Interneuron deficits in patients with the Miller-Dieker syndrome. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2005 Mar 1; [Epub ahead of print].
Pilz DT, Matsumoto N, Minnerath S, Mills P, Gleeson JG, Allen KM, Walsh CA, Barkovich AJ, Dobyns WB, Ledbetter DH, Ross ME. LIS1 and XLIS (DCX) mutations cause most classical lissencephaly, but different patterns of malformation. Hum Mol Genet. 1998 Dec;7(13):2029-37.
Tai CY, Dujardin DL, Faulkner NE, Vallee RB. Role of dynein, dynactin, and CLIP-170 interactions in LIS1 kinetochore function. J Cell Biol. 2002 Mar 18;156(6):959-68. Epub 2002 Mar 11.
Tanaka T, Serneo FF, Higgins C, Gambello MJ, Wynshaw-Boris A, Gleeson JG. Lis1 and doublecortin function with dynein to mediate coupling of the nucleus to the centrosome in neuronal migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Jun 7;165(5):709-21. Epub 2004 Jun 01.
Williams SN, Locke CJ, Braden AL, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA. Epileptic-like convulsions associated with LIS-1 in the cytoskeletal control of neurotransmitter signaling in C. elegans. Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Sep 15;13(18):2043-59. Epub 2004 Jul 14.
Zhang G, Assadi AH, McNeil RS, Beffert U, Wynshaw-Boris A, Herz J, Clark GD, D'Arcangelo G. The Pafah1b Complex Interacts with the Reelin Receptor VLDLR. PLoS ONE. 2007 Feb 28;2:e252.
|
